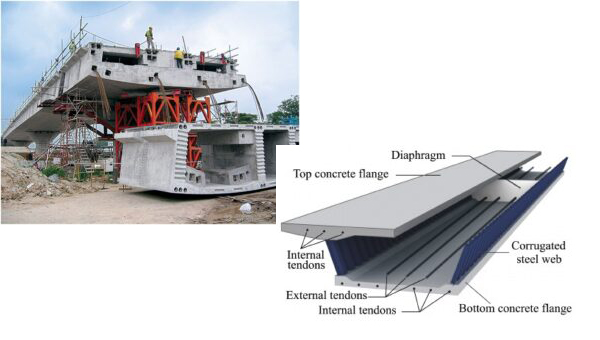
TEE - BEAM BRIDGES
A T-beam bridge is a structural element able to withstand large loads by resistance in the beam or by internal reinforcements. In some respects, the T-beam dates back to the first time a human formed a bridge with a pier and a deck. After all, a T-beam is, in one sense, no more than a pillar with a horizontal bed on top, or, in the case of the inverted T-beam, on the bottom. The upright portion carrying the tension of the beam is termed a web or stem, and the horizontal part that carries the compression is termed a flange. However, the materials used have changed over the years but the basic structure is the same. T-beams structures such as highway overpasses, buildings and parking garages, have extra material added on the underside where the web joins the flange to reduce the T-beam’s vulnerability to shear stress. However, when one investigates more deeply into the design of T-beams, some distinctions appear.
The T-beam bridge though simple in design, contains multiple design elements of interest. Unlike an I-beam, a T-beam lacks a bottom flange, which carries savings in terms of materials, but at the loss of resistance to tensile forces. In parking garages, however, it is obvious that this lack of a bottom flange on a T-beam actually serves as an advantage in that the stem rests on shelf making the flange the upper deck. T- beam bridge designs come in many sizes, lengths and widths depending on what the structure is and its compression tension needs